Health is better than wealth. Part 2
Останнє редагування: 2015-03-12
a) At the chemist’s. Medicines.
|
Chemist/ druggist/pharmacist |
[ˈkemist [fɑ͟ː(r)məsɪst] |
аптекар |
| Pills/tablets | [pillz / tæ̱bləts ] |
пілюлі |
| Drug | [drʌ̱g] | ліки, медикамент; засіб |
| Powder (f.e. stomachache powder) | [pa͟ʊdə(r)] | порошок |
| Drops (f.e. eye drops) | [drɒ̱ps] | краплі |
| Mixture (f.e. Cough/Cold Relief) | [mɪ̱kstʃə(r)] | суміш, мікстура |
| Injection | [ɪnʤe̱kʃ(ə)n] | ін’єкція |
|
Ointment/(antiseptic) cream |
[ɔ͟ɪntmənt] | мазь |
| Soothing/ sedative/ analgetic | [su͟ːðɪ̱ŋ][se̱dətɪv] | обезболююче |
| Aspirin | [æ̱spɪrɪn] | аспірин |
| Valerian |
[vəˈlɪərɪən] | валерьяна |
| Penicillin | [pe̱nɪsɪ̱lɪn] | пеніцилін |
| Iodine | [a͟ɪ͟ədiːn, AM -daɪn] | йод |
| Bandage | [bæ̱ndɪʤ] | пов’язка через плече |
| Sling | [slɪ̱ŋ] | бинт, пов’язка |
| Cotton(wool) | [kɒ̱t(ə)n w'ʊl] | бавовна,вата |
| Plaster | [plɑ͟ːstə(r), plæ̱s-] | гіпс |
| Sticking plaster | [stɪ̱kɪŋ] | лейкопластир |
| Mustard plaster | [mʌ̱stə(r)d] | гірчичник |
| Hot-water bottle/bag | [hɒ̱t wɔ͟ːtə(r) bɒ̱t(ə)l] | грілка |
| Thermometer | [θə(r)mɒ̱mɪtə(r)] | градусник, термометр |
| (Eye) glasses/ spectacles/ goggles | [ˈspektəkəlz][gɒ̱g(ə)lz] | окуляри/ захисні окуляри |
| Stretcher | [stre̱tʃə(r)] | носилки (для хворих) |
|
Ambulance |
[æ̱mbjʊləns] |
машина швидкої допомоги |
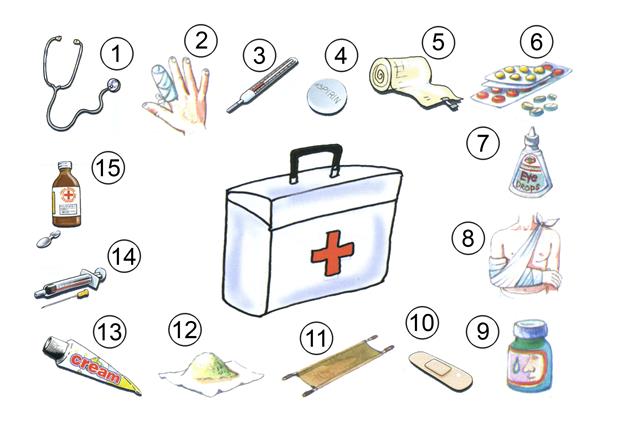
Task 11 Fill in the gaps with the correct words.
( bandage, a thermometer, pills, , a sticking plaster, cotton wool, a stretcher, cough relief mixture, ointment, eye drops, plaster, scissors, stomachache powder )
1. We use ______to cut plasters, bandage etc, to the required (потрібний) size.
2. We use ______ ______ to clean wound.
3. We use ______ to wrap around a cut on part of the body to stop it bleeding.
4. We use ______ ______ to treat an eye infection.
5. We use ______ for a variety of purposes in the form of antibiotics, vitamins etc,
6. We use ______ to treat wounds or sore areas.
7. We use ______ to take our temperature.
8. We use ______ to carry a critically- ill patient.
9. We use ______ to treat a stomachache.
10. We use ______ ______ ______to treat a bad cough.
11. We use ______ to put on a cut finger.
12. We use ______ to put on a broken leg or arm.
Task 12 You are going on a beach holiday. Decide which of the following you would pack in the first aid kit. You can add your own ideas. Use the model:
A: I think (I don’t think) we need to pack some aspirin.
B: I absolutely agree (You are right). We’ll need them in case we get a headache.
Task 13 Antibiotics [æ̱ntibaɪɒ̱tɪks]
What are antibiotics? They are important medicines as they help fight infections caused by bacteria [bæktɪ͟əriə]. However, bacteria find ways to resist antibiotics, so that they no longer work. The more we use antibiotics, the less effective they become, so we should use them carefully.
How to use antibiotics?
Don’t use antibiotics if you don’t need them. If you have a virus, antibiotics won’t work. Since viruses [va͟ɪ͟ərəsiz] cause all colds and most sore throats and cough you should ask your chemist for advice rather than take antibiotics.
When are antibiotics the answer?
Your doctor will prescribe antibiotics when you need them, for example, for pneumonia. Remember, antibiotics are more likely to work when you really need them.
Agree or disagree with these statements.
1. Antibiotics are very important medicines.
2. They can be used to fight with a virus.
3. We shouldn’t use antibiotics because it isn’t effective.
4. Bacteria cause colds and sore throats.
5. Patients can use antibiotics only if the doctor advises to do it.
6. Pneumonia can be cured only with the help of antibiotics.
Answer the questions
1. Why are antibiotics important medicines?
2. Should a patient take antibiotics if he has a cough?
3. Who can prescribe you antibiotics?
4. What is the most effective way of curing pneumonia?
5. When is it necessary to use antibiotics?
a) Names of specialists.
|
Physician / doctor Therapist Pediatrician Dentist Ear/throat doctor / otolaryngologist Eye doctor / ophthalmologist Heart doctor / cardiologist Gastroenterologist Traumatologist Surgeon Nerve-specialist Nurse
|
[fɪzɪ̱ʃ(ə)n] [θe̱rəpɪst] [pi͟ːdiətrɪ̱ʃ(ə)n] [de̱ntɪst] [ˌəʊtə(ʊ)larɪŋˈgɒlədʒist] [ɒ̱fθælmɒ̱ləʤɪst] [kɑ͟ː(r)diɒ̱ləʤɪst]
[sɜ͟ː(r)ʤ(ə)n] [nɜ͟ː(r)v spe̱ʃəlɪst] [nɜ͟ː(r)s] |
лікар терапевт педіатр зубний лікар отоларинголог офтальмолог кардіолог гастроентеролог травматолог хірург невролог медична сестра
|
Task 14 Complete the sentences.
1) If you have a headache, you consult a … .
2) If something has got into your eye, you go to see an … .
3) If you have a sore throat, you consult a … .
4) If you have a heart attack, you call a … .
5) If you catch the grippe, you are attended by a … .
6) If your nerves are out of order, you consult a … .
7) If your little sister or brother has a high temperature, you send for a … .
8) If you have got a deep cut in your finger, you should attend a … .
9) If you have broken your arm or leg, you are taken care of by … .
10) If you have some problems with your stomach or liver, you consult a … .
11) If you have a toothache, you consult a … .
12) If you have a scald, a burn, a bruise, a bump or a blister, you consult a … .
Task 15
A. Look at the pictures and use the prompts to say what health problems each person seems to have, as in the example:
I think Ann has a backache.
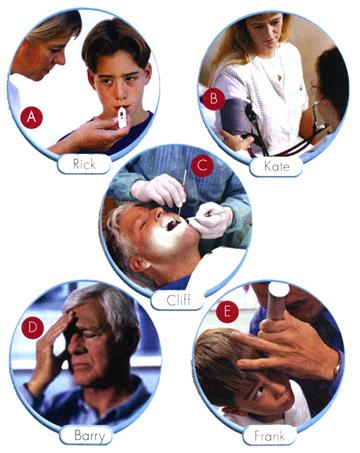
B. Now say what you would do if you had one of these health problems.
Example: If I had a backache, I would consult a traumatologist.
C. Speak about the last medical checkup at your school. Who did it, your school doctor or different specialists? Don’t forget to mention the procedure of the examination. What advice did the doctor or the nurse give you?
g) Basic units of a hospital.
| Emergency unit | [ɪmɜ͟ː(r)ʤ(ə)nsi ju͟ːnɪt]] | прийомне відділення |
| Intensive care unit | [ɪnte̱nsɪv ke͟ə(r)] | відділення реанімації |
|
Intermediate care unit |
[ɪ̱ntə(r)mi͟ːdiət] |
терапевтичне відділення |
|
Surgical unit |
[sɜ͟ː(r)ʤɪk(ə)l] | хірургічне відділення |
| traumatological | |
травмотологичне |
| Medical records department | [me̱dɪk(ə)l re̱kɔː(r)dz] | реєстратура |
| Laboratory | [ləbɒ̱rətri] | лабораторія |
| Foodservice department | [sɜ͟ː(r)vɪs dɪpɑ͟ː(r)tmənt] | харчовий блок |
| Pharmacy | [fɑ͟ː(r)məsi] | аптека |
| Pediatric unit | [pi͟ːdiətrɪk] | педіатричне відділення |
Task 16 Match the names of the hospital units with their functions.
| 1. Emergency unit | a. doing tests | |
| 2. Food service department | b. keeping records of patients | |
| 3. Intensive care unit | c. making and selling drugs | |
| 4. Intermediate care unit | d. performing operations | |
| 5. Laboratories |
e. preparing meals | |
| 6. Medical records department |
f. treating all kinds of patients | |
| 7. Pediatric unit | g. treating children | |
| 8. Pharmacy | h. treating critically ill patients | |
| 9. Surgical unit |
i. treating those who have suddenly become ill |
Task 17 Answer the questions (TS21, page 188, Our English 7, L.Byrkun)
Which unit do children stay in?
Which unit serves critically ill people?
Which unit cares for patients waiting for an operation or after it?
Which unit cares for people who suddenly become ill?
Which unit cares for different kinds of patients?
Which unit provides medicines?
Which unit prepares meals for patients?
Which unit conducts tests?
Which unit keeps records of the patients? Why is it also very important?
Task 18 An ambulance has taken these people to hospital. Read the information about them and decide which unit of the hospital they will get to.
1. Ann is 30. She has scolded her hand.
2. Alice is 13. She has fractured her arm.
3. Jane is 24. She got into a car accident.
4. Pete is 9. He has sprained his ankle.
5. Lillie is 12. She has a bad stomachache.
6. Thomas is 60. He suddenly felt a pain in his heart.
7. Harry is 8. He has a bad earache.
8. Barbara is 32. She has problems with her back.
9. John is 15. He was playing football and broke his right leg.
10. Liza is 50. She has got pneumonia.
h) Bodily Defects.
|
Disabled / handicapped |
[disabled / hæ̱ndikæpt] |
з фізичними вадами |
|
Blind |
[bla͟ɪnd] |
сліпий |
|
Deaf |
[de̱f] |
глухий |
|
Mute / dumb |
[mju͟ːt / dʌ̱m] |
німий |
| Deaf and dumb | глухонімий | |
| Lame | [le͟ɪm] | кульгавий |
|
Bad/poor eyesight |
[a͟ɪsaɪt] |
поганий зір |
|
Long-/far-sighted |
[lɒ̱ŋ /fɑ͟ː(r) sa͟ɪtid] |
далекозорий |
| Short-/near-sighted | [ʃɔ͟ː(r)t / nɪ͟ə(r) sa͟ɪtid] | короткозорий |
| Cross-eyed | [krɒ̱s a͟ɪd] | косоокий |
Task 19 Answer the questions using the words: lame, blind, long-/far-/sighted, deaf and dumb.
|
When is a man unable
|
to play football? to read a newspaper at a short distance? to cross the street alone? to speak? to become a sportsman? |
Task 20 Match the parts of the dialogues:
| 1. I’ve got a terrible headache. | a) You should eat regularly. And not chips, but healthy meals. | |
| 2. I’ve caught a cold. |
b) You shouldn’t eat too much chocolate. | |
| 3. I’ve got a stomachache. | c) You shouldn’t eat too much ice cream. | |
| 4. I’ve got a sore throat. | d) Here. Take the temperature. | |
| 5. I’ve got an earache. | e) You shouldn’t watch TV late. | |
| 6. I’ve got a toothache. | f) You should wear a hat. It’s cold. |
Task 21 Look at the pictures and act out the dialogues:
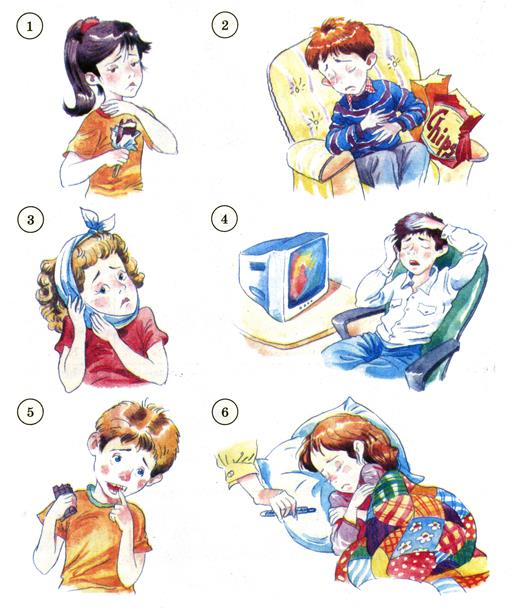

Task 22 Compose short stories referring to every picture.
Task 23 Answer the questions:
1. What can happen if you eat too much chocolate and sweets?
2. What can happen if you play computer games long?
3. What can happen if you drink cold water?
4. What can happen if you eat unhealthy food?
5. What can happen if you don’t wear a hat in cold weather?
6. What can happen if you stay up late?
Task 24 Answer the questions:
1. What should you do to keep your teeth healthy?
2. What should you do to have good eyesight?
3. What should you do not to have a stomachache?
4. What should you do not to have a headache?
5. How do you feel when you catch a cold?
6. What should you do when you catch a cold?
Task 25 Give all possible answers.
- What do you do if you witness an accident?
a) I ask after the health of the victim.
b) I telephone for an ambulance.
c) I rush off to the hospital.
d) I offer all kinds of medicine.
- What do you do if your friend has a heart attack?
a) I ask, ”How do you feel?”
b) I nurse her/him.
c) I give her/him some drops.
d) I put a compress on her/his heart.
e) I call a doctor.
- What do you do if you have liver trouble?
a) I keep a diet.
b) I often feel sick / have attacks of sickness.
c) I go to see a doctor regularly.
d) I take long walks.
- What do you do if you cut your finger?
a) I send for a doctor.
b) I bandage it.
c) I ask to be put on a sick-list.
d) I take my temperature,
e) I lie in bed.
- What do you do if you begin to recover from an illness?
a) I go to a sanatorium.
b) I suffer from sleeplessness.
c) I tell everybody I am better.
d) I have no appetite.
e) I put on weight.
Task 26 Match the words to make up pairs. Model: a catching disease
a) Person, temperature, throat, child, cold, headache, heart, pulse, disease, illness
b) Catching, quick, chronic, sick, sore, normal, weak, bad, slight
Task 27
A). Match the medical problems with the kinds of doctors who treat them.
E.g. When I have a stomachache I first go to a family doctor and then to a gastroenterologist.
| 1. You can’t hear well. | a. dentist |
| 2. You can’t see well. |
b. ear doctor/ otolaryngologist |
| 3. You feel pain in the heart. |
c. eye doctor/ophtalmologist |
| 4. You feel pain in the knee. | d. heart doctor / cardiologist |
| 5. You have broken your arm. |
e. pediatrician |
| 6. You have a headache. |
f. surgeon |
| 7. You have a sore throat. | g. therapist |
| 8. You have a stomachache. |
h. traumatologist |
| 9. You have a toothache. | i. gastroenterologist |
| 10. You have a backache. |
|
| 11. You have a scald. | |
| 12. You have food poisoning. | |
| 13. You have a cut. | |
| 14. You have a bruise or a blister. |
B). Make up short dialogues as in the model:
- You look pale. What’s the matter with you? (What’s the trouble?)
- I am not very well. I have a backache.
- You should consult a traumatologist.
Task 28 Match the names of the hospital units with their functions.
| 1. Emergency unit | a. doing tests | |
| 2. Food service department | b. keeping records of patients | |
| 3. Intensive care unit | c. making and selling drugs | |
| 4. Intermediate care unit | d. performing operations | |
| 5. Laboratories |
e. preparing meals | |
| 6. Medical records department |
f. treating all kinds of patients | |
| 7. Pediatric unit |
g. treating children | |
| 8. Pharmacy | h. treating critically ill patients | |
| 9. Surgical unit |
i. treating those who have suddenly become ill |
Task 29 A) Match the halves and read some English proverbs about health.
| 1. A sound mind |
a. after supper walk a mile. | |
| 2. After dinner sit a while | b. but eat to live. | |
| 3. An apple a day | c. have desperate cures. | |
| 4. Desperate diseases must | d. in a sound body. | |
| 5. Early to bed and early to rise |
e. is above wealth. | |
| 6. Good health |
f. is the best medicine. | |
| 7. Laughter | g. keeps the doctor away. | |
| 8. Live not to eat |
h. is worth two after | |
| 9. One hour’s sleep before midnight | i. makes a man healthy, wealthy and wise. |
B) Translate the proverbs from Ukrainian into English.
1. У здоровому тілі здоровий дух.
2. Хто рано встає, тому Бог дає.
3. Здоров’я дорожче за багатство.
4. Після обіду посидь, а після вечері пройдись.
5. З'їдай в день по яблоку, і лікар тобі не знадобиться.
6. Клин клином виганяють.
7. Сміх – найкращі лікі.
8. Година сну до півночи варта двох після.
9. Живи не для того, щоб їсти, а для того , щоб жити.
Task 30 The statements are wrong. Correct them.
Model : - People use pills when they cut a finger.
- Oh, no, they don’t/they never do. They use iodine when they cut a finger.
a) Doctors use a thermometer when they fill a tooth.
b) Doctors use iodine when they treat for pneumonia.
c) People use eye-glasses when they have an ear-ache.
d) People use a bandage when they take their temperature.
e) People use iodine when they are short-sighted.
f) People use cotton when they have a cough.
g) People use pills when they put a compress.
h) People use a stretcher when they have a cold in the head.
Task 31 Read the texts and answer the questions. At the doctor’s
1. Ann’s story.
When people feel bad they should consult a doctor. If you have a high temperature, it’s better to call a doctor. The doctor examines you carefully. He feels your pulse, sounds your heart and lungs, checks your blood pressure, examines your throat and tongue. If the throat is red and it’s difficult to swallow and to breathe, it may be flue, quinsy, or just a bad cold. Whenever a person has a cold he often coughs and sneezes.
Then the doctor prescribes some medicine for a sore throat and for a headache. If the doctor prescribes a medicine for you, you should take it regularly. He usually advises to drink warm milk with butter, honey or mineral water. And, certainly if you fall ill, you should stay in bed for some days at least. If you follow the doctor’s advice, you will recover soon. Otherwise you may have serious complications.
I want to tell you about the accident which happened to my grandfather. He is sixty-seven years old. For the last five years he has had problems with the heart. But one day he felt very bad and we immediately called for the ambulance. It arrived very quickly and took my granddad to hospital. The cardiologist told us that he had a heart attack. It was very dangerous for his life. But the doctors made all necessary injections quite in time and saved his life. He stayed in hospital for a month and the doctors treated him in a professional way. Now my granddad feels well.
What do people usually do when they feel unwell?
What is it better to do when you have a high temperature?
How does the doctor examine the patients?
What are the symptoms of a bad cold?
Is it necessary to follow the doctor’s advice? Why?
What happened to the grandfather one day?
What did the members of the family do immediately?
How long did the old man stay in hospital?
How does the granddad feel now?
1. John’s story.
There is nothing more unpleasant than being taken ill when you are away from home. During my stay in Great Britain I suddenly fell ill. I felt hot and I was in a high fever. I had a splitting headache and my throat was sore too. I had no appetite I took a pill of aspirin, went to bed and fell asleep. In the morning I wasn’t better. I had a high temperature and all my body ached. My friend looked at me and telephoned the doctor’s office. The doctor examined me and said that there was nothing serious, probably I had caught cold. But he decided to take me to hospital to go through necessary tests there. I was brought to hospital by an ambulance.
At hospital they checked my blood pressure, took my blood test and X-rayed my chest. I was given some medicine for my cough, throat, headache and fever. These were cold relief pills, cough relief drops, injections, and some mixtures for gargling (полоскання) the throat. I had some electrical treatments and mastered plasters were put on my chest. They nursed me very well. I had to stay in hospital for seven days and leaving it I was quite well again.
1. What happened to John during his stay in Great Britain?
2. What were the symptoms of his illness?
3. What did he take for his headache, cough, fever, sore throat?
4. Did the aspirin help him?
5. Who called for the doctor?
6. What was the doctor’s diagnosis?
7. Why was he taken to hospital?
8. How did they examine the patient at the hospital?
9. What was the medical treatment of the patient?
10. Were there any complications after the illness?
11. How did John feel after leaving hospital?
Task 32 Fill in gaps
P__ ys__tion pat__ __nt s__ __geon
Bl__ __d pre__sure ambul__nce stoma__ __ache
H__art atta__ __ doct__r thro__t
In__ect__on __ __armacy pediatri__ __an
Heada__ __e tempera__ __re tre__t
M__d__cine co__gh pn__um__nia
__ __emist
Task 33 Divide this long word into the smaller ones:
Ambulancepatienttemperaturehealthappetitecoughheadachestomachsoreprescriptionpul
sebreathointmentchemistphysiciandumbdiagnosisdiagnosedeafsurgeonwoundthermome
tertonguesanatoriumtroubleiodinetuberculosisscarletfevermeaslespneumoniacurableincurable
Task 34 Unscramble the words.
1. pehl __ __ __ __
2. tocdor __ __ __ __ __ __
3. trhu __ __ __ __
4. ntmeteatr __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
5. ryjuin __ __ __ __ __ __
6. ealhth __ __ __ __ __ __
7. cidimene __ __ __ __ __ __ __
8. uecr __ __ __ __
9. nesslli __ __ __ __ __ __ __
10. seadise __ __ __ __ __ __ __
11. icsk __ __ __ __
12. nipa __ __ __ __
Task 35 Fill in the gaps with one word.
a) If you feel unwell, first of all it is necessary to turn to the p__________ .
b) The doctor e_________ you carefully.
c) The doctor p_________ medicines.
d) The doctor t__________ sick people.
e) It’s very i__________ to follow the doctor’s directions.
f) Every day s_________ make operations, strugling for p_________s’ lives.
g) Experienced doctors and n_________ work day and night to help sick people.
Task 36 Give derivatives (похідні слова), word combinations and expressions and make up sentences with them:
sleep nerve cough examine ill operate treat prescribe consult
Task 37
A. Give the opposites to:
1. far- sighted
2. medicines for internal use
3 to take off a compress
4 to undress a wound
5 the temperature rises
6 to feel well
7 to be out of bed
B. Make up sentences using the phrases and the opposites to them.
Task 38 Read aloud and give Ukrainian equivalents of the following:
| A) |
B) | ||
| 1. sick-leave |
1. To have a bad cough |
8. To suffer from sleeplessness | |
| 2. examination |
2. To consult a doctor |
9. To be treated for pneumonia | |
| 3. recovery |
3. To see one’s tongue |
10. To take pills for a backache | |
| 4. headache |
4. To take one’s temperature |
11. To recover from a cold | |
| 5. to sneeze | 5. To have a pain in the chest |
12. Curable diseases | |
| 6. to breathe |
6. To feel one’s pulse |
13. Catching diseases | |
| 7. chemist |
7. To die of TB | 14. To feel an ache in the bones |
C)
1. What is the trouble?
2. What’s the doctor’s diagnosis?
3. Take a table spoonful three times a day.
4. You don’t look at all good.
5. Must I stay in bed?
6. I am so-so.
7. What are the directions (instructions) for use?
8. This treatment did me (a world of) good.
9. I wish you a quick recovering.
Task 39 Match the exchanges, then read out the dialogue.
1. Are you okay Peter? You look a bit pale.
2. What’s the matter?
3. Have you got a temperature?
4. It sounds like you’ve got flu.
5. If I were you, I’d go straight home to bed.
a) Yes, I’m burning up, and my whole body aches.
b) What shall I do, then?
c) Actually, I feel terrible.
d) That’s a good idea. I’ll do that.
e) I’ve had a headache for days.
Task 40 A. Act out the dialogues.
1. - What’s the matter with your arm, Ann? Why is it in a sling?
- I was careless while boiling the milk this morning and scalded it. I didn’t know what to do, so I ran to the polyclinic, and the nurse there put some ointment on it and bandaged it. It is much better now, and I think it won’t blister.
2. - Why are you limping (кульгати), John? What is the matter?
- I was playing football yesterday and sprained my ankle(вивихнув щиколотку). It hurts badly. I can hardly walk, as you see.
- You mustn’t walk at all. Lie down and put compresses on your ankle. That’s the best remedy (засіб лікування). Call the doctor and he will give you a sick-leave for a few days.
3 - May I come in, doctor?
- What is the matter with you, my boy.
- Something is wrong with my knee. It hurts.
- Let me have a look at it. Hm… It’s a splinter (скалка, скіпка). You’ve come just in time you avoid an infection and an abscess. Well, let me remove the splinter. …Everything is all right. Now the nurse will bandage up the knee.
- When can the bandage be removed? Can I do it myself tomorrow morning?
- If you do, dirt will get in, the knee will swell up and you’ll have to be operated on.
4 - Hello, Peter. What is the problem?
- Well, I haven’t been feeling well for the last two days.
- I see.
- And my throat is sore and it hurts when I swallow.
- Have you noticed the loss of appetite?
- Not really. But it’s difficult to swallow.
- Right then, let me look… mmm…yes your throat is quite inflamed. We’d better take your temperature.
- Actually, I do feel a bit warm.
- Hmm… just as I thought… 38.5° C. I’d say you’ve got tonsillitis. Are you taking any medicine at the moment?
- No, not really.
- There’s nothing to worry about, really. I’m going to give you a prescription. Make sure you drink lots of hot fluids and soup, nothing cold.
Pediatric unitOK, thanks a lot.
5. - When was the last time you saw your doctor?
- About two months ago.
- What was the problem?
- I had the flu.
- How did you feel? Can you describe your symptoms?
- I had a temperature and my muscles ( [mʌ̱s(ə)lz]мускули ) ached,
- What did the doctor advise you to do?
- She advised me to drink lots of fluids ([flu͟ːɪdz] рідина) and stay in bed.
B. Make up your own dialogues and act them out.
Task 41 Fill in the article where necessary.
A day’s wait
He came into the room to shut (1) … windows while we were still in bed and I saw he looked ill. He was shivering, his face was white and he walked slowly as though it ached to move.
“What’s (2) … matter, Schatz?”
“I’ve got (3) … headache.”
“You’d better go back to bed.”
“No, I’m all right.”
“You go to bed. I’ll see you when I’m dressed.”
But when I came downstairs he was dressed, sitting by the fire, looking (4) … very sick and miserable boy of nine years old. When I put my hand on his forehead I knew he had (5) … fever.
When (6) … doctor came he took (7) … boy’s temperature. It was one hundred and two. (8) … doctor left three different medicines in different coloured tablets with instructions for giving them.
One was to bring down (9) … fever. He said there was nothing to worry about if (10) … fever did not go above one hundred and four degrees. There was (11) … light epidemic of flu and there was no danger if you avoided pneumonia.
I wrote (12) … boy’s temperature down and made (13) … note of the time to give … tablets.
I sat at (14) … foot of (15) … bed.
“Why don’t you try to go to sleep? I’ll wake you up for (16) … medicine.”
“I’d rather stay awake.”
After a while he said to me, “You don’t have to stay in here with me, Papa, if it bothers (набридло) you.”
I thought perhaps he was a little light-headed (в маренні) and after giving him (17) … prescribed tablets at eleven o’clock I went out for a while.
When I returned they said the boy had refused to let anyone come into the room.
I went up to him and found him in exactly the same position I had left him, white-faced, but with the tops of his cheeks flushed by (18) … fever, staring still (все ще уставившись), as he had stared, at (19) … foot of (20) … bed.
“How long will it be before I die?”
“You aren’t going to die. What’s (21) … matter with you?”
“Oh, yes, I’m. I heard (22) … doctor say (23) … hundred and two. “
“People don’t die with (24)… fever of one hundred and two. That’s (25) … silly way to talk.”
“I know they do. At school in France the boys told me you can’t live with forty-four degrees. I’ve got (26) … hundred and two.”
He had been waiting to die all day, ever since nine o’clock in the morning.
“You poor Schatz,” I said. “Poor old Schatz. It’s like miles and kilometers. That’s (27) … different thermometer. On that thermometer thirty-seven is normal. On this kind of thermometer it’s ninety-eight degrees.”
‘Are you sure?”
“Absolutely,” I said. “It’s like miles and kilometres. You know how many kilometres we make when we do seventy miles in the car?” ( mile – миля = 1609,33 metres )
“Oh,” he said.
But his gaze (пильний погляд) at (28) … foot of (29) … bed relaxed slowly.
The next day he cried very easily at little things that were of no importance. (Ernest Hemingway)
- What happened to Schatz?
- What were the symptoms of his illness?
- How did the boy feel?
- How high was his temperature?
- What were the medicines prescribed by the doctor for?
- What epidemic was there when the story happened?
- Who was taking care of the boy?
- Why didn’t the boy go to sleep? What was he waiting for?
- What made the boy think that he was going to die?
- What fever (temperature) can people die with?
- What kinds of thermometers are in use nowadays?
Kinds of thermometers
- centigrade [ ] стоградусний термометр Цельсія; 36.6 degrees centigrade
- Fahrenheit thermometer [ ] термометр Фаренгейта; 50°,60° … ; f.e. 50 degrees Fahrenheit
- Reaumur thermometer [ ] термометр Реомюра
Task 42 A. Safety activities at home:
1. Never use a chair, a table or a pile of boxes if you need to get something from the upper shelf. Use a ladder and ask someone to hold it for you if possible.
2. Never leave toys, shoes and other things on the floor. Keep everything in its place. This will help you to prevent falls.
3. To prevent cuts, keep kitchen knives in a knife rack.
4. Never pick up broken glass with your bare hands. Use a wet towel to pick up anything that is left.
5. Always keep the floors dry, so that nobody falls down.
6. Don’t burn or scald yourself or others while cooking. Never run when carrying anything hot or sharp.
7. Turn pot handles to the back of the cooker. If a handle sticks out, a child may take it.
- 8. To prevent falls in the bathroom, use a rubber mat and keep soap in a holder.
- 9. When you fill a bath, always put in the cold water first. This will help you to prevent scalds.
- 10. Keep drugs away from the children. When you take a medicine, read the instructions carefully. Never take medicines belonging to someone
- 11. Electric tools must be used carefully, too. Do not touch anything electrical if your hands are wet. Do not take anything electrical to the bathroom.
What dangers can wait for you at home?
B. Safety activities at school:
- 1. Don’t run along the corridors. You can fall down and break your leg or arm. You can also push other pupils and hurt them.
- 2. Don’t push or hit your schoolmates. You may hurt them.
- 3. Don’t awing your arms and legs. You can hurt somebody.
- 4. Be careful while climbing up and down the staircases. Hold on the handrail. You may fall down and fracture your legs and arms. Try not to kick somebody downstairs.
- 5. Don’t fight with your schoolmates. You will have bruises and scratches.
- 6. Never throw anything on the floor. Somebody may fall down because of this.
- 7. Walk slowly when the floor in the corridor or in the classroom is wet after washing.
- 8. Don’t eat your meals with dirty hands. You can have a stomachache.
- 9. While having meals in the school canteen don’t scald other pupils with hot tea or soup.
What dangers can wait for you at school?
C. Safety activities in the street:
- 1. Cross the streets only at street crossings.
- 2. Obey traffic lights. Cross the street only when the light is green.
Never cross the street when the light is red.
- 3. Before crossing the street stop and look both ways.
- 4. Go across the road quickly but don’t run.
- 5. Never play in the street.
What dangers can wait for you in the street?



